Introduction
Urban planning has been contributing to the formation of healthy urban environments, preventing disorganized urban sprawl and encouraging infrastructure development in Japan. However, urban areas in Japan, which is facing depopulation and aging society, are at a big turning point. New social issues such as a rapid increase of empty apartments and lands, and non-universal design of facilities lie heavily on their sustainable development, especially regional area. On the other hand, excessive concentration of people due to the relocation of people and the increase of industries in Tokyo still continues. Efficient urban management is required, and municipalities recognize the significance and importance of compact urban development from the perspective of administrative costs.
From this kind of circumstance, the Japanese government strongly promotes i) formation of a high-quality urban renovation project for regional hub cities, ii) consensus building among those concerned, and iii) investor’s understanding, according to the concepts “Selection and Concentration” and “Respect for Local Intention”.
Recently, the investment climate has changed dramatically with the expansion of the Internet and the development of information communication technologies such as “Fin-Tech”. Information-intensive activities are very important to call for investment.
The “i-Urban renovation and planning” is an information infrastructure for urban renovation and renewal. It allows people to analyse and to visualize the situation and problems of urban areas according to the future vision of each area using geospatial information and virtual reality technologies. The quantitative analysis and visualization clearly shows the cash-flow and spatial plan of the city and promotes understanding and encourages consensus building among relevant players, e.g. investors, citizens, and developers.
This document defines the encoding specification of the data for i-Urban renovation and planning (which is called “i-Urban renovation and planning Data), and aims to assist the formation of social agreement and to improve the quality of urban investment in order to contribute to urban renovation and renewal.
The i-Urban renovation and planning Data is the combination of following data:
a) 3-dimentional city objects and city model
b) Detailed information of city objects for analysis
c) Constraints/conditions (e.g. regulation) related to urban renovation
d) Statistical grid data for demand and supply analysis
e) Global city model for global analysis and visualization
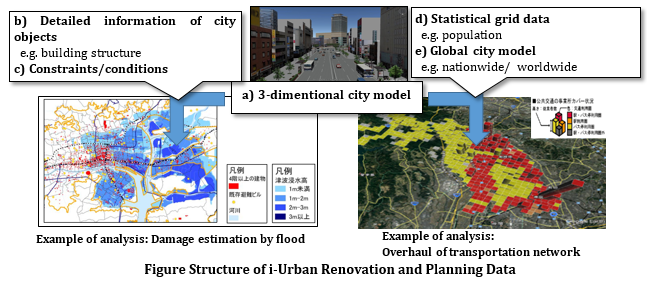
The i-Urban renovation and planning Data Encoding Specification targets on b) to e) data, as a) is already defined in City Geography Markup Language (CityGML). CityGML is an XML/GML based 3D data standard for the representation, storage and exchange of 3D city models and is widely used in the application fields related to urban areas.
The i-Urban renovation and planning Data Encoding Specification is composed of four parts listed below. Each encoding specification is tied up with each component and is an extension of CityGML according to the rules of the Application Domain Extensions (ADE) to ensure data interoperability. Thus i-Urban Planning Data aims to be utilized in various application fields, such as disaster prevention, tourism and to carry out urban renaissance.
| Part 1: Urban Object Data Encoding Specification This document targets on b) Detailed information of city objects for analysis and define them as properties of CityGML object. |
|
| Part 2: Urban Function Data Encoding Specification This document targets on c) Constraints/conditions related to urban renovation and define constraints and conditions as subclasses of the root class in CityGML. |
|
| Part 3: Statistical Grid Data Encoding Specification This document targets on d) Statistical grid data for demand and supply analysis and define a statistical grid as subclasses of the root class in CityGML. |
|
| Part 4: Extended LOD Data Encoding Specification for Global City Model This document targets on e) Global city model for global analysis and visualization. To promote “compact cities”, global analysis and visualization are necessary for role sharing among cities, and global city model which is easy to handle is also required. Therefore this document defines new Levels of Detail (LOD) for a broad description of city models CityGML already supports different LODs. LODs are required to reflect independent data collection processes with differing application requirements. This document extends LODs to describe rough city models which do not have to be detailed but should be described with a unified unit among cities. This enables users to analyse cities under the same conditions. |
Urban Object Data Encoding Specification
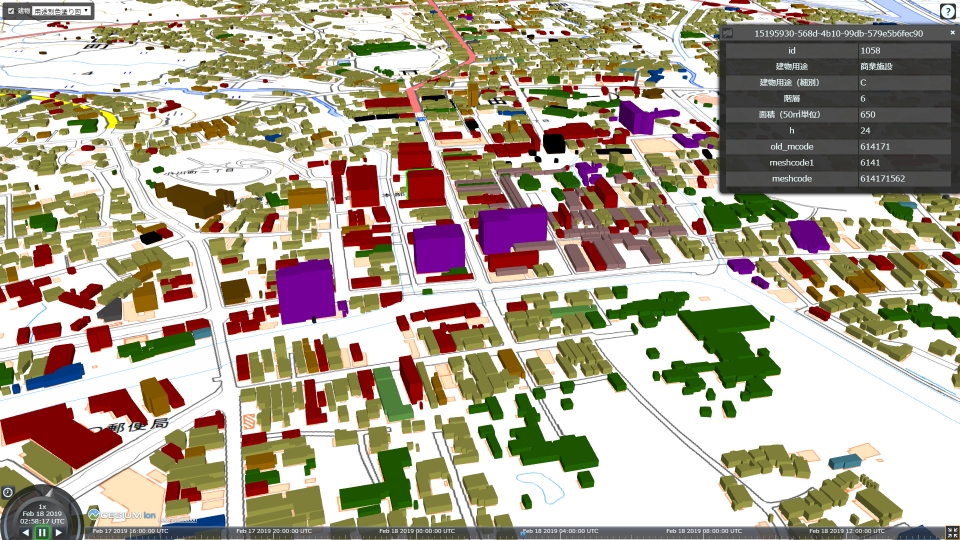
Detailed information of buildings, roads, and other objects which constitute urban areas are necessary for the quantitative assessment of the current situation and problems in urban areas.
This document defines additional information of urban objects which is necessary for urban assessment as attributes of urban objects and specifies the encoding format of the information.
[clink url=”http://kashika-new-dev.kashika.net/40220-munakata-building/”] [clink url=”http://kashika-new-dev.kashika.net/20214-chino-building/”]Urban Function Data Encoding Specification
Plans and regulations are important information in urban development, landscape preservation, and disaster management. Information related to plans and regulation, such as administrative boundaries and zoning works, are conditions or constraints for spatial planning and are conceptual and virtual objects in urban areas.
This document defines conceptual and virtual objects in urban areas as “urban function objects” and specifies the encoding format of these objects.
[clink url=”http://kashika-new-dev.kashika.net/40220-munakata-building/”]Statistical Grid Data Encoding Specification
To grasp the current situation and issues of urban areas, it is necessary to compare the same area at different points of time or different areas with the same conditions. The universal standard is necessary for time-series analysis.
This document defines statistical grid for time-series analysis and regional comparison, and specifies the encoding format of statistical grid.
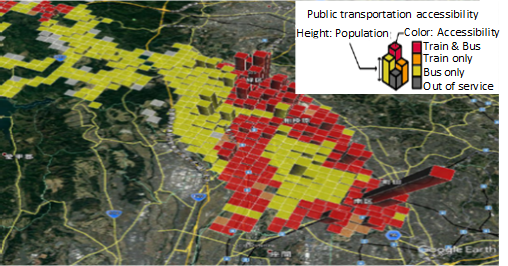
The Statistical grid module enables users with time-series analysis and regional comparison . A grid is a network composed of two or more sets of curves, in which the members of each set intersect the members of the other sets in an algorithmic way, and the curves separate space into grid cells. Statistical grid module gives statistical values to each grid cell.
Extended LOD Data Encoding Specification for Global City Model
Global city model is necessary for comparing cities and understanding the relationships between cities through quantitative assessment. This is necessary in order to clarify the current situation and problems in urban areas.
The global city model does not have to be in detailed but should be described with a unified unit among cities, which enables users to analyse cities under the same conditions.
This document defines the mechanism to describe the global city model and specifies the encoding format of the information.
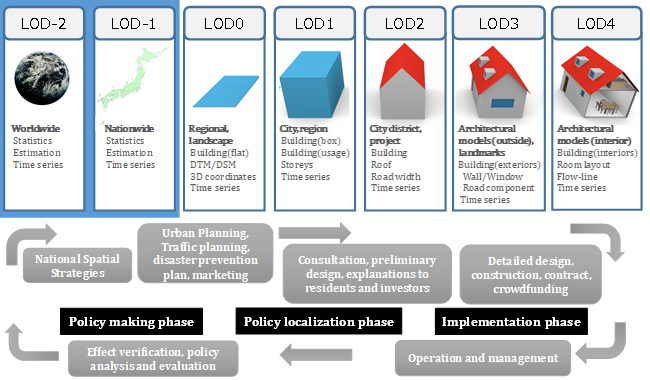
The Extended LOD Data Encoding is an extension of CityGML. CityGML supports different Levels of Detail (LOD) and defines five levels of detail (LOD 0 to 4).
This document defines two extra LODs which enables users to use global city models for comparison and analysis among cities without any inconsistency between LOD0 to 4.
The level LOD-2 is for describing worldwide city models and the level LOD-1 is for nationwide city models. City objects such as buildings, roads, and water bodies are not identified as objects in LOD-2 and LOD-1 but parts of the surface. These levels are coarser than LOD0 and suitable for statistical analysis and future estimation .

コメント